The drilling mud circulating system components comprises the following equipment:
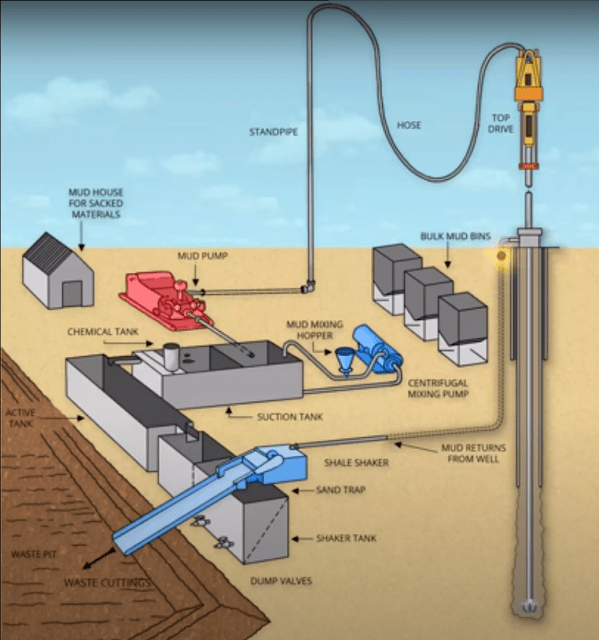
- Active Tank(s)
- Reserve Tanks
- Sand Traps and Process Pits
- Slug and Pill Tanks
- Trip Tank & Stripping operation Tank
- SCE (Solids Control Equipment)
- Mixing System
Active Tank

This is the tank from which drilling fluid is pumped downhole and to which drilling fluid returns from the hole is received. The route taken by the drilling fluid when circulating is called the active (circulating) system. At the start of circulation, the Mud Pumps are lined up on the Active Tank, and drilling fluid is pumped to the Stand Pipe Manifold on the drill floor. The drilling fluid then travels up the Stand Pipe and Kelly Hose to the Swivel or top drive in the drilling rig (TDS), both of which suspend the drill string and allow it to rotate independently from the Kelly Hose. Overhead View of Mud Tanks and Mud Pumps. From there, the drilling fluid travels down the drill string to the drill bit, picking up drilled cuttings and carrying them up the annulus between the drill string and the well bore. A Bell Nipple underneath the drill floor sends the drilling fluid returns from the hole along a flow line that leads to the Scalping Shaker and Shale Shakers, which remove most of the drilled cuttings. The drilling fluid then passes through the Sand Traps and Process Pits, which contain additional Solids Control Equipment to remove smaller-sized solids in the drilling fluid. The cleaned-up mud then flows back to the Active Tank to complete the circulating system.

Reserve Tanks In Drilling Mud Circulating System
These are used for storing fluids according to requirements. Reserve mud is usually prepared or stored in these tanks or different fluids in preparation for the next phase (e.g. oil-based mud or completion brine).
Sand Traps and Process Tanks In Drilling Mud Circulating system
The Sand Traps are usually positioned below the shale shakers and act as settling pits for the drilling fluid after passing through the shale shakers. The drilling fluid then passes through the Process Tanks, comprising degasser, desander, desilter, and centrifuge tanks. As the names suggest, these tanks contain degassers and solids control equipment for removing smaller-sized particles from the drilling fluid before being returned to the active tank.
Slug and Pill Tanks
These tanks are more minor than active and reserve tanks. They are used for preparing “slugs” (high-density mud that is pumped into the drill string before tripping out of the hole) and pills to address particular situations (e.g. an LCM pill to control formation losses, a unique mix to improve drilling mud properties, etc.).
Trip Tank and Stripping Tank
The Trip Tank is a tall, narrow tank located near the flow line and used for accurately monitoring drill pipe displacement volumes while tripping pipe in or out of the hole. Active drilling mud from the Trip Tank is circulated across the hole, and valves in the flow line near the Bell Nipple are realigned to send the fluid returns back to the Trip Tank, forming a very small circulating system. Pipe displacement causes the Trip Tank to fill up when running in the hole (RIH) and to empty when pulling out of the hole (POH), so it needs to be emptied or filled at regular intervals while tripping. The Stripping Tank is smaller than the Trip Tank and is used for monitoring pipe displacement volumes when stripping in or out of the hole when the Annular Bag Diverter is closed.
SCE (Drilling Solids Control Equipment) In Mud Circulating system
It is essential to minimize the build-up of solids in a drilling fluid because they affect drilling performance and can encourage hole problems. A range of equipment is available for removing solids from the drilling fluid, some or all of it found in the following order: Scalping Shaker, Shale-Shakers, Desander, Desilter, Mud Cleaner, and Centrifuges.
Mixing System
The mixing system is used to build and treat drilling fluids and prepare slugs and pills. Equipment includes centrifugal pumps and mix hoppers and may include pressurized surge tanks for adding bulk Bentonite or Barite. Fluids can usually be mixed in active, reserve, slug, or pill tanks. The mix pumps are also used for transferring fluids to other rig parts (e.g., to the trip tank, cement unit, sand traps, etc.), or for backloading fluids to a road tanker or supply boat.