The water-based fluid may contain chlorides from the base fluid (e.g., Sodium or Potassium Chloride) or may pick up chlorides while drilling. Chloride Test Drilling Mud is useful for determining any unexplained changes in water-based mud salinity because an increase or reduction in salinity will indicate salt or water contamination. So, It is important to have chlorides in drilling mud.
The Equipment Required For Chloride Test Drilling Mud:
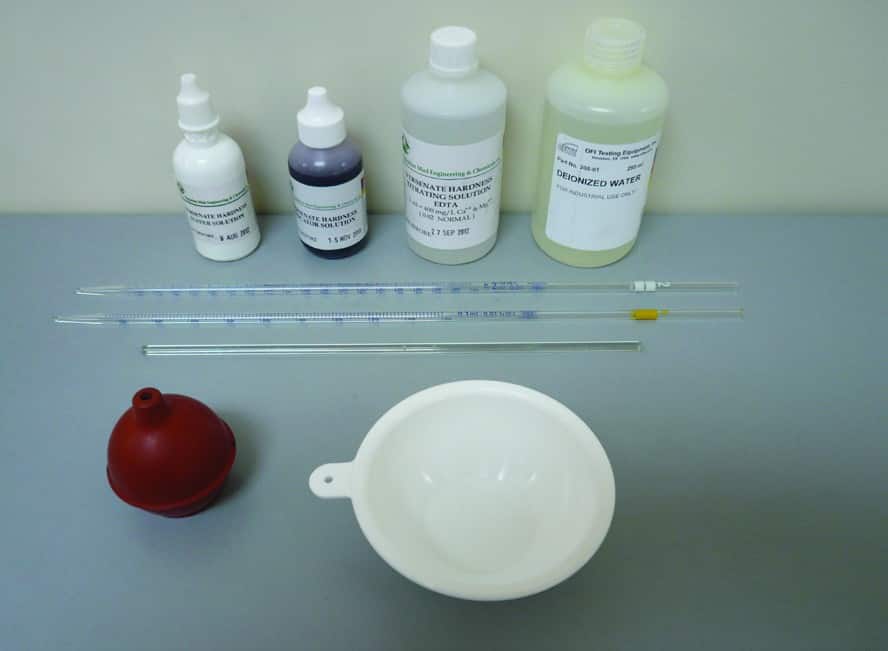
The equipment required for Chloride Test Drilling Mud is as follows:
- Phenolphthalein indicator solution
- Sulfuric or Nitric Acid, 0.02N
- Potassium Chromate indicator solution
- Silver Nitrate solution, 0.0282N or 0.282N, depending on mud salinity
- Distilled Water
- Titration dish (white ceramic crucible)
- Glass stirring rod or magnetic stirrer with magnet
- Graduated pipette, 1 ml x 0.01 ml graduations
- Graduated pipette, 10 ml x 0.1 ml graduations
The procedure for measuring chlorides is as follows:
- Pipette 1 ml filtrate into a titration dish containing around 25 ml distilled water.
- Add five drops of Phenolphthalein indicator solution, and if the indicator turns pink, then add 0.02N Sulfuric or Nitric Acid (drop by drop), stirring the sample with a glass stirring rod until the pink color disappears.
- Add around ten drops of Potassium Chromate indicator solution, turning the fluid yellow.
- Use a glass rod or magnetic stirrer with a bar magnet to stir the solution continuously while adding Silver Nitrate solution with a pipette until the yellow color turns to orange-red and persists for 30 seconds (Use 0.0282N AgNO3 for chlorides below 10,000 mg/l and 0.282N for chlorides above 10,000 mg/l).
- The chloride concentration in mg/L can be calculated according to the AgNO3 strength used for the titration. See Figure 9 below
A larger water or filtrate sample volume should be used for checking fluids with low chlorides, as this will give a more accurate measurement (e.g., titrate with a 10 ml sample when checking the chlorides in mix water).
Chlorides should be around 175,000 to 185,000 mg/L in salt-saturated mud systems.
For Chlorides below 10,000 mg/l:
Chlorides, mg/l = 1,000 x (ml of 0.0282N AgNO3) / (ml of filtrate used)
For Chlorides above 10,000 mg/l:
Chlorides, mg/l = 10,000 x (ml of 0.282N AgNO3) / (ml of filtrate used)