Drill Bit Pressure Drop Calculation
Calculating hydraulic horsepower and impact force depends on calculating pressure drop across the bit. When jet bits are used, a significant percentage of normal circulating pressures is lost by pumping through the nozzles. The pressure loss is not frictional pressure but rather acceleration forces. Assumptions generally made are:

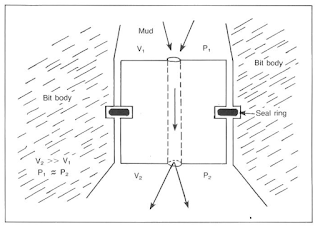
1) the changes in pressure resulting from a change in elevation are negligible.
2) the upstream velocity (V.) is negligible compared to downstream (as below figure).
Based on these assumptions, the bit pressure drop is calculated according to the below Equation:
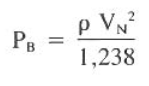
Solving for nozzle velocity, VN:
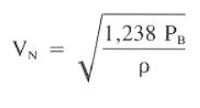
Laboratory studies show the pressure drop through the nozzle does not correspond precisely according to Eqs. above. As a result, a discharge coefficient factor, Cd is applied to make laboratory results correspond to theoretical pressure drops. The discharge coefficient will vary, depending on nozzle type and size, A value of 0.95 is representative, however, for most field situations.
Applying Cd above equation becomes:
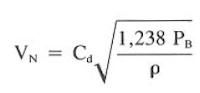
The velocity in the nozzles is equal to the flow volume divided by the area, or V = Q/A
Converting to standard field units, the VN becomes as follows:
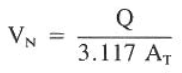
Where:
AT = total nozzle area, in^2
Q = flow rate, gal/min
VN = nozzle velocity, ft/sec
Using Eq. 1&2 And solving for PB:
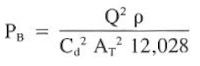
Drill Bit Hydraulic Horsepower & Impact Force Calculation
Hydraulic Horsepower at the drill bit
A measure of the energy per unit of time expended across the bit nozzles. It is commonly calculated with the equation HHP=P*Q/1714, where P stands for pressure drop in pounds per square in., Q stands for flow rate in gallons per minute, and 1714 is a conversion factor necessary to yield HHP in horsepower. Bit manufacturers often recommend that fluid hydraulics energy across the bit nozzles be in a particular HHP range, for example, 2.0 to 7.0 HHP, to ensure adequate bit tooth and bottom-of-hole cleaning (the minimum HHP) and to avoid premature erosion of the bit itself (the maximum HHP).
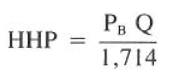
Impact Force Calculations at the drill bit
Impact pressure, which affects impact force, is the momentum change of the drilling fluid distributed over the impacted area at the hole bottom. This pressure, acting downward and to the sides, attempts to overcome chip hold-down pressure and remove cutting from beneath the bit. Pressure and remove cutting from beneath the bit.
In drilling Hydraulics, Impact Force can be calculated through this equation.
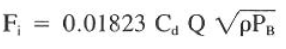
Example On How To Calculate bit pressure drop, Hydraulic Horse, Power And Impact Force
Calculate the drill bit pressure drop, hydraulic horsepower, and impact force for the following set of conditions:
- Mud weight = 14.5 Ib/gal
- Flow rate = 300 gal/min
- Jet sizes = three 12/32 in. jets
Solution:
1. Determine the nozzle area, AT:
AT = 3 x π /4 x (d)^2 = 0.331 in^2
2. Eq.3 is used to calculate the pressure drop at the bit:
PB= (300)^ 2 x 14.5 / ( 0.95^2 x 0.331 ^2 x 12028) = 1097 psi
3. Calculate the hydraulic horsepower expended at the bit from Eq.4
HHP = (1097 psi x 300 gal/min) / 1714 = 192 hp
4. The hydraulic impact force due to pressure loss through the drilling bit is computed from Eq.5
Fi = 0.01823 x (0.95) x (300) x ((14.5)(1,097))^(1/2) = 654 Ib
Finally, Drill Bit Pressure Drop Calculators Online
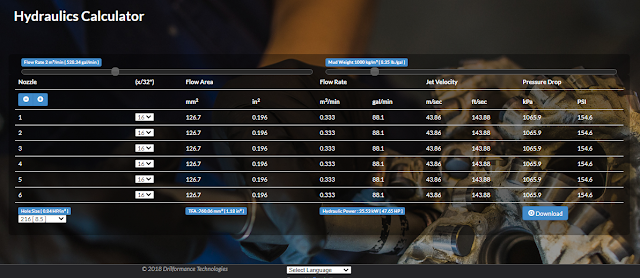
DrillFormance Online Drill Bit Pressure Drop Calculator
Pacesetter Online Drill Bit Pressure Drop Calculator
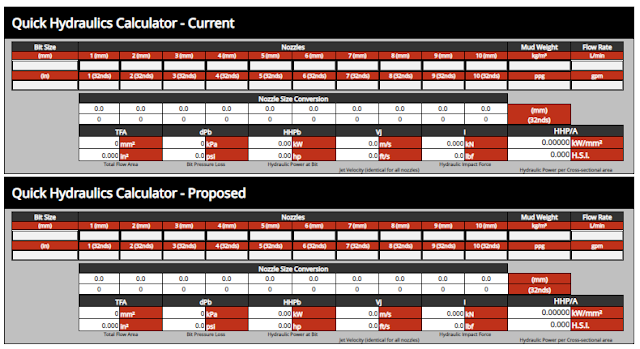
Pressure Drop Online Calculator Fot Bit Pressure Drop Calculation