
Cementing Unit:
The cementing unit is a high-pressure pump used to force cement down the casing and into the annular & space between the casing and the open hole wall.
Cementing units are usually adapted with mixers, pumps & drives to provide on-site cement mixing and injection inside the well, especially for oil and gas drilling operations. The cementing operations prevent water invasion into the drilled well, provide isolation to the annulus after running the casing string, and can also be used to pump & set cement plugs to isolate certain zones or shut in the well.
Cementing units shall be able to provide an acceptable range of pressures and pumping rates to provide the requirements of recent cementing practices and, of course, have the lowest applicable weight-to-horsepower ratio to facilitate transportation.
Cementing Unit Components:
To understand the inspection process of such a cementing unit, we will have to go through the cementing unit components.
Cementing units are usually prepared with two positive-displacement pumps.
- For a high-pressure system, one pump mixes the cement while the other pushes the cement inside the well.
- A centrifugal pump mixes the slurry for a low-pressure system, and two positive-displacement pumps are used for displacement.
- One centrifugal pump provides water to the mixing jet for recirculating mixing, and another recirculates slurry back through the mixing jet. As with a low-pressure system, two positive-displacement pumps are used to get the slurry and displace it down the well.
Motor, transmission, and pumps:
A heavy-duty electric-powered engine or petrol related to a transmission supplies mechanical energy to drilling mud pumps, water pumps, and agitators.
Mostly, all the cementing pumps are positive-displacement pumps, and it is common to find duplex double-acting piston pumps or single-acting triplex plunger pumps. Either is satisfactory within its design limits. Triplex pumps discharge more smoothly for heavy-duty pumping and can usually handle higher horsepower and more significant pressure than duplex pumps. Most cementing work involves a maximum pressure of less than 5,000 psi, but pressures as high as 20,000 psi are not uncommon. Because of widely varying operating conditions, the cementing pump and its power train are designed for the maximum rather than the average expected pressures.
Mounting platform:
Cementing units utilized in the oilfield can be trailer-mounted or truck-mounted. Cementing units can be established on skids, which causes them to be more appropriate for in-situ applications, such as in marine drilling rigs. Also, it can be mounted on waterborne vessels.
Control system:
The cementing operator has panel-mounted controls to easily adjust flow rate, cement slurry density, and different cementing unit parameters. Many cementing units include hydraulic and digital gauges to help operators observe all cementing operations.
The Mixing System:
Water and cement slurry reservoirs converge in the mixing tank earlier than being dispensed via unit outlets and hoses through pumps. A cleaning system can clean any remaining cement slurry.
The cementing job determines which sort of cementing unit will be more applicable. A modular design is favorable for oil rigs because it has to meet size, safety, and power constraints.
Purposes of Cementing Unit Inspection Test
- Verify the hydraulic integrity of the Cementing Unit, cementing lines, and manifold at the maximum working pressure.
- Verify the flow rate, mixing, and power capability of the Unit.
Guideline for Cementing Unit Pressure Test.
- If the Drilling Contractor has its procedure, follow those procedures.
- Be sure that all the components of the Cementing Unit are pressure tested to the working pressure:
- Cement unit manifold,
- Cementing lines,
- Rig floor cementing manifold.
- Attach to the report a schematic drawing of the cementing manifold system with the result of the test.
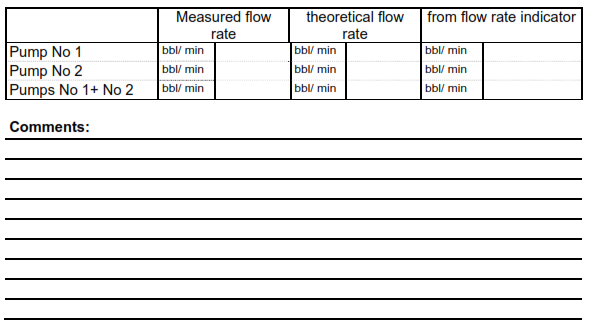
Guideline for Cementing Unit Flow rate tests.
- Fill up the two tanks of the cementing unit with water.
- With one pump, start pumping at the maximum possible flow rate, taking water from each cementing unit tank alternatively and refilling the empty tank with the rig centrifugal pumps.
- Repeat the same operation with the other pump of the cement unit.
- Repeat, if possible, the same operation with the two pumps together.
- Fill in the following table.
Other Items To Put In Mind While Rig Accepting For Cement Unit
Cementing Unit :
- State of maintenance satisfactory :
- Date of unit’s last general overhaul :
Cementing unit discharging lines
- Number and dimension as per contract :
- Rigid section satisfactory :
- Flexible section satisfactory :
- Connected as per contract drawing :
Rig floor cement Manifold :
- State of maintenance satisfactory :
- Same type of valves