Safety joint can be used in drilling, fishing, drill stem testing, washover or any pipe string. It is a threaded connection with coarse threads or other special features that will cause it to unscrew before other connections in the string. It is one of the great tools that have been used in oil and gas rigs since long time. We can use them whenever and wherever there is a need for a releasing safety connection.

Generally, safety joints is a two-piece special connection located at any desired point in a pipe string. It will withstand all of the regular operations of the string, transmit full torque in either direction, or, at the operator’s will, it can be quickly released to salvage all of the portions of the string above it.
Application
We generally use them in any where you need a safe releasing joint for your operations.
- In Fishing, its is recommended to place it above the fishing tool and below jar or bumper sub.
- We can use it between the washover string and the drill pipe.
- In drilling, we can place them in the drill string above the drill collar to keep it away from compression stresses and to avoid sticky formations.
- In Drill stem test, safety joint to be placed above the packer.
- Placing it above the packer will facilitate disengaging in case of packer stuck.
Drill Pipe Safety Joint
Made up at any desired point in a drilling, fishing, testing, wash-over, or tubing string, the drill pipe safety joint operates as a unit unaffected by vibration, the inertia of the drilling bit, or drill collars, or while rotating out of the well. No movement can occur between its two sections, nor can it be released without a specific mechanical procedure. When the need arises, it is simple to disengage and to reengage.
Drill pipe Safety Joints have drill pipe box and pin connections with the O.D. and I.D. corresponding to the drill pipe tool joints.
Components
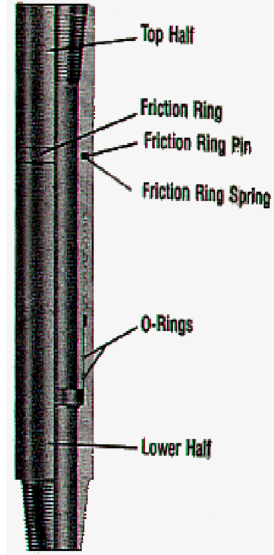
Generally, it consists of an upper Pin Section, a lower Box Section, and two Packers. The upper Pin Section has a box connection up for connecting to the tool joint and a helical male thread down for connection to the Box Section. The Box Section has a broad helical female thread matching the Pin Section’s male thread and a tool joint pin connection down for connecting to the pipe.
The broad helical matching threads of the Pin and Box Sections allow speed and ease of engagement since they are relatively free of contact as the two sections are made up. However, when the Safety Joint is bade up tightly, the reversely pitched surfaces of the joining shoulders grip each other securely, pulling the mating helical surfaces into complete contact and forming the Safety Joint into a rigid unit.
The Pin Section is grooved at the top and bottom to accommodate the “O” ring-type Top and Bottom Packers, which seal the Safety Joint from internal and external fluid pressures. Both Packers are rated for high-pressure operation, capable of withstanding more than 10,000 psi in continuous service.
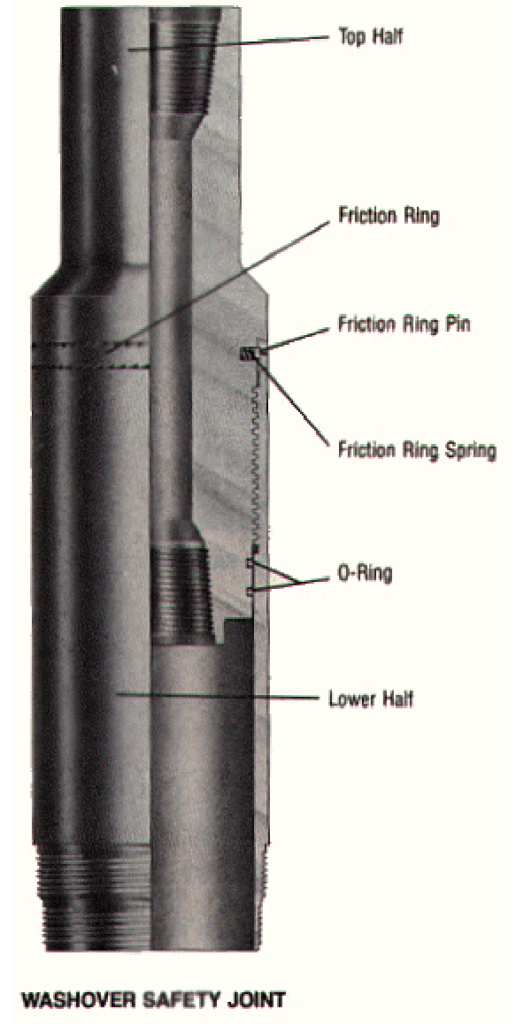
Washover Safety Joint
The washover type connects the drill pipe to the washover string, allowing for easy release of the drill pipe if there is a pipe sticking problem.
Two types of safety joints are used with a washover string. One, a standard type, will unscrew at seven to nine rounds to the left if the washpipe becomes stuck. The other is a washover/backoff-type. Unscrewing this safety joint takes 15 to 17 rounds to the left. Without it, the washpipe could unscrew completely while trying to back off the fish. If this happens, the fish can be retrieved, but the washpipe will be left in the well.
Washover safety joints are manufactured from heat-treated alloy steel and must exceed the strength of the pipe it is connected to. To ensure proper functioning, it should be assembled correctly in the string. This can be achieved by connecting the lower half to the wash pipe and then connecting the top half to the lower half with the same torque as was used for the wash pipe connections.
The lower half of the washover safety joint remains with the wash pipe when parted and is a full bore to match the wash pipe, making subsequent re-entry of other tools possible. A coarse pitch safety thread, in combination with the friction ring, assures proper release when required.
How to Release The Safety Joint
Please consider that this is general releasing procedure.
- Firstly, break the its connection with the drill string by applying left-hand torque. (40% of its makup torque)
- Secondly, POOH with the string gradually while rotating to the left to unscrew the safety joint. Don’t rush as to avoid any jump in the string.
- During applying the torque, the string weight will decrease.
- This will unscrew the upper part from the lower part.
Note: The retrieved upper half will still contain the friction ring.
How to Reengage
Please consider that it is a general reengaging procedure.
- Tag slowly & feel for contact between the pin section and the lower part box section.
- Apply a small amount of weight.
- Make one turn to the left, then gradually to the right while maintaining weight on it.
- Observe the torque, once it starts to increase , this will indicate that the joint is still making up & engaging.
External Links
- NorthEast Oil Well Partners Product Manual
- Bowen Manual
- Aramco Drilling Best Practice Book